스프링 부트3 제 12장
서비스? 롤백? 문제가 생기면 그 전으로 되돌린다고요?
스프링 부트3 제 12장
서비스(Service)
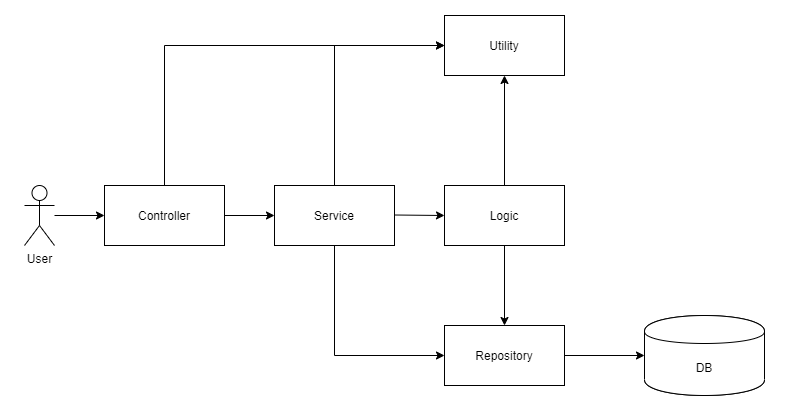
컨트롤러와 리파지터리 사이에 위치하는 계층으로, 서버의 핵심 기능(비즈니스 로직)을 처리하는 순서를 총괄한다. 대략적인 흐름은 아래와 같다.
서비스 계층 만들기
ArticleApiController
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
// ... 생략
// GET
@GetMapping("/api/articles")
public List<Article> index() { // 모든 게시글 보기
return articleService.index();
}
@GetMapping("/api/articles/{id}")
public Article show(@PathVariable Long id) { // 단일 게시글 보기
return articleService.show(id);
}
// POST
@PostMapping("/api/articles")
public ResponseEntity<Article> create(@RequestBody ArticleForm dto) { // 게시글 쓰기
// RequestBody는 본문에 실어 보내는 데이터를 메서드의 매개변수로 받아올 수 있게 하는 어노테이션
Article created = articleService.create(dto);
// 삼항 연산자(게시글 생성에 성공하면 정상, 실패하면 오류 응답
return (created != null) ?
ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(created) :
ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).build();
}
// PATCH
@PatchMapping("/api/articles/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Article> update(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody ArticleForm dto) { // 일부 데이터만 수정할 경우
Article updated = articleService.update(id, dto);
return (updated != null) ?
ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(updated) :
ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).build();
}
// DELETE
@DeleteMapping("/api/articles/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Article> delete(@PathVariable Long id) { // 단일 게시글 삭제
Article deleted = articleService.delete(id);
return (deleted != null) ?
ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT).body(deleted) :
ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).build();
}
기존의 articleRepository가 하던 일을 ArticleService가 담당하도록 분업했다.
ArticleService
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
// ... 생략
@Slf4j
@Service // 서비스 객체 생성
public class ArticleService {
@Autowired
private ArticleRepository articleRepository; // 게시글 리파지터리 객체 주입
public List<Article> index() { // 모든 게시글 반환
return articleRepository.findAll();
}
public Article show(Long id) { // 단일 게시글 반환
return articleRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
public Article create(ArticleForm dto) { // 게시글 생성
Article article = dto.toEntity();
if (article.getId() != null) { // article 객체에 id가 존재한다면 null 반환(기존 게시글 수정을 막기 위해)
return null; // id는 DB가 생성하기 때문에 필요 없음
}
return articleRepository.save(article);
}
public Article update(Long id, ArticleForm dto) { // 게시글 수정
// 1. 수정용 엔티티 생성
Article article = dto.toEntity();
log.info("id: {}, article: {}", id, article.toString());
// 2. DB에 대상 엔티티가 있는지 확인
Article target = articleRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
// 3. 잘못된 요청 처리
if (target == null || id != article.getId()) { // DB에 데이터가 없거나 URL의 id와 게시글의 id가 맞지 않는 경우
log.info("Error! id: {}, article: {}", id, article.toString());
return null;
}
// 4. 있으면 업데이트하고 정상 응답 보내기
target.patch(article);
Article updated = articleRepository.save(target);
return updated;
}
public Article delete(Long id) { // 게시글 삭제
// 1. 대상 찾기
Article target = articleRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
// 2. 잘못된 요청 처리
if (target == null) {
return null;
}
// 3. 대상 삭제
articleRepository.delete(target);
return target;
}
}
ctrl + /를 누르면 선택한 라인이 모두 주석 처리된다.
트랜잭션(Transaction)
모두 성공해야 하는 일련의 과정을 뜻한다. 쪼갤 수 없는 업무의 최소 단위이기도 하다.
트랜잭션 수행 과정 중 실패할 경우, 진행 초기 단계로 되돌리는 것을 롤백(rollback)이라고 한다.
트랜잭션 맛보기 코드
ArticleApiController의 transactionTest() 메서드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@PostMapping("/api/transaction-test")
public ResponseEntity<List<Article>> transactionTest(@RequestBody List<ArticleForm> dtos) {
List<Article> createdList = articleService.createArticles(dtos);
return (createdList != null) ?
ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(createdList) :
ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).build();
}
ArticleService의 createArticles() 메서드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
@Transactional // 해당 메서드는 하나의 트랜잭션으로 묶임
public List<Article> createArticles(List<ArticleForm> dtos) { // 트랜잭션 테스트를 위한 메서드
// 1. dto를 엔티티로(스트림 문법 활용)
List<Article> articleList = dtos.stream()
.map(dto -> dto.toEntity())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 2. 엔티티를 DB에 저장
articleList.stream()
.forEach(article -> articleRepository.save(article));
// 3. 강제로 예외 발생시킴
articleRepository.findById(-1L)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("결제 실패"));
// 4. 결과 값 반환
return articleList;
}
@Transactional 어노테이션을 통해 메서드를 하나의 트랜잭션으로 만들 수 있다.
어노테이션이 없을 경우, 각 과정은 따로 수행되어 3번 과정에서 오류가 발생했음에도 DB에 데이터가 들어간 것을 볼 수 있다.
어노테이션이 있을 경우, 각 과정은 하나의 트랜잭션으로 취급되어 3번에서 오류가 발생하면 DB에 들어갔던 데이터가 다시 롤백된다.
스트림 문법은 배열 같은 자료구조를 순회하며 처리하는 코드 패턴이다.
for() 문 같은 반복문을 더 짧게 줄여 쓸 수 있다.
이 기사는 저작권자의 CC BY 4.0 라이센스를 따릅니다.